Attention problems are a common secondary effect of brain injury. They can make it challenging to complete everyday tasks, maintain conversations, and affect your performance at work or school. Fortunately, concentration skills can often be improved after a brain injury, and this post will show you how.
To help you understand attention problems after brain injury, this article will discuss:
- What is attention?
- Causes of attention problems after brain injury
- Signs of attention problems
- How to treat attention problems after brain injury
- Helpful tips for improving attention
What is Attention?
Teachers have been asking students to “pay attention” for years. However, the concept of attention is more complex than it initially seems. There are many types of attention that may be affected due to a brain injury. These include:
- Arousal attention: being generally alert to your surroundings.
- Sensory attention: focusing on something using a specific sense. For example, in a crowded room, you would need visual attention skills to search for a friend, and auditory attention skills to concentrate on a conversation with that friend rather than background noise.
- Executive attention: choosing how to filter what is important enough to focus on. This can include the use of selective attention (choosing just one thing to focus on, such as one particular fish in an aquarium) and divided attention (focusing on multiple things, such as when driving and talking on the phone at the same time).
Depending on the location of your brain injury, you may have more difficulties with certain types of attention than others. In the following section, we’ll discuss how brain damage in certain areas of the brain can cause attention problems.
Causes of Attention Problems After Brain Injury
Different areas of the brain control different functions. To understand the cause of attention problems after brain injury, we can look at the specific areas of the brain that contribute to one’s ability to pay attention.
One area of the brain that plays a major role in attention is the lateral intraparietal cortex. This area lets a person visually focus on specific objects while filtering out other stimuli.
For example, the lateral intraparietal cortex is what allows you to pay attention to the road and relevant environmental information (road signs, other cars, etc) when driving. When this region is damaged, it may become challenging to filter out competing sensory stimuli. Individuals may struggle to drive within their lane or fail to pay attention to traffic lights and street signs. As a result, everyday tasks like driving may no longer be safe for individuals after brain injury due to attention problems.
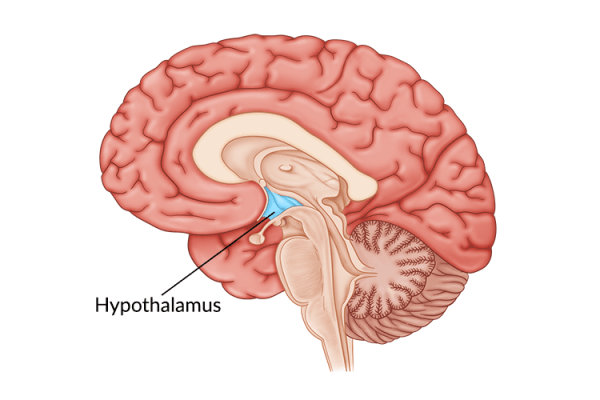
Damage to other areas of the brain such as the prefrontal cortex, visual cortex, thalamus, and midbrain can also contribute to attention deficits. These are not the only factors, though. There are other conditions that can make it challenging for an individual with a traumatic brain injury to concentrate.
Other causes of attention problems after brain injury include:
- Cognitive or physical fatigue
- Sleep disorders
- Headaches
- Emotional problems, such as mood swings or depression
- Lack of vitamin B and other vital brain nutrients
Treating these underlying issues can often drastically improve your concentration skills. In the following section, we’ll discuss how to spot attention difficulties.
Signs of Attention Problems After Brain Injury

Attention difficulties after brain injury may contribute to other cognitive problems including difficulties with memory, problem-solving, and communication. This can affect interactions with others and the ability to perform self-care independently.
An individual with attention problems after brain injury may experience the following challenges:
- Difficulty listening to others talk
- Trouble reading an article or book chapter all the way through
- Difficulties following the plot of a movie
- Struggling to finish a task
- Inability to multitask (such as listening to music and washing the dishes)
Fortunately, even if you have serious attention problems, it is possible to find techniques to manage them and improve your concentration. In the following section, we’ll discuss various interventions that can help individuals improve their focus following a brain injury.
How to Treat Attention Problems After Brain Injury

Attention can be affected in many ways following a brain injury. As a result, a personalized approach to treatment that focuses on each individual’s specific attention deficits is ideal.
Below, we’ll go over some of the best practices for improving concentration skills after brain injury:
1. Focus on Your Overall Health
As we mentioned above, sometimes it’s not just cognitive issues that lead to attention problems. Lack of sleep, a poor diet, pain, stress, and side effects from medications may contribute to attention problems. Therefore, along with other specific treatments, it can help to also focus on your overall health to maximize recovery.
The mind and body are closely connected. If you keep your body healthy, you’ll likely notice your mental strength improving as well. Here are a few tips that can help you improve overall health:
- Exercise regularly. Try to get at least 30 minutes of exercise every day. Exercise helps promote circulation to the brain, which can improve overall cognitive and physiological functioning.
- Eat a healthy brain injury diet. What you eat can significantly affect your ability to focus. Try to also incorporate important vitamins for brain injury, which may help supplement essential vitamins and minerals lacking in your current diet.
- Get enough sleep. Sleep repairs brain cells and helps the brain recharge so it can focus throughout the day. If you have trouble falling or staying asleep, consult with a sleep specialist.
- Stay hydrated. If your brain doesn’t get enough water, it may affect your ability to concentrate. Try to drink at least 64 oz per day.
2. Work with a Cognitive-Behavioral Therapist
One of the most effective ways to improve attention after a brain injury is to work with a psychologist that specializes in cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy focuses on identifying the situations in your daily life that can be affected by attention problems and encouraging more effective ways to manage them.
Simple strategies like writing things down, setting reminders on your phone, and reiterating what is going on during a conversation can help you work through attention problems.
3. Practice Attention Exercises Consistently
Consistent practice plays a crucial role in improving attention skills after brain injury. The brain has an adaptive healing mechanism called neuroplasticity, which allows it to rewire itself and relearn functions affected by injury. The best way to promote it is through consistently practicing the skills you want to improve.
Repetitively practicing attention exercises helps stimulate the brain and reinforces demand for attention skills. The more you practice, the stronger the neural pathways for that function become.
4. Download Cognitive Therapy Apps
An excellent way to practice attention exercises is to download a cognitive therapy app on your phone or tablet. For example, the CT Speech and Cognitive Therapy App includes over 100,000 exercises designed by speech-language pathologists to help improve cognitive skills like attention after a neurological injury.
Having access to attention exercises whenever you need them can empower you to practice more repetitions throughout the day. The CT app’s smart artificial intelligence technology helps ensure that the exercises you’re practicing are just the right difficulty level to keep you engaged and optimize your results.
5. Ask Your Doctor About Medications
If your attention problems are severe, ask your doctor about medications that may help improve your ability to focus. However, medications may not be ideal for all individuals due to potential side effects, so do not take any without permission from your physician.
Now that you understand some of the most effective ways to improve attention problems, let’s discuss helpful tips to keep in mind when practicing attention exercises.
Helpful Tips for Improving Attention After Brain Injury
To improve attention after brain injury, focus on making simple changes to your everyday routine. Although they may not seem like much, they can yield significant results.
Here are three tips that can help you manage your attention problems and improve your concentration:
- Clear your environment. It helps if you make your work as distraction-free as possible. When you need to focus, try to keep your desk organized, turn off the TV or radio, and use noise-canceling headphones or earplugs.
- Start small. If your attention problems make it challenging for you to focus for more than a few minutes, try breaking whatever you are working on into smaller tasks. This helps make each task more approachable and less overwhelming.
- Build up slowly. Once you break an activity down to a manageable level, start gradually increasing the load. You should feel challenged, but not overwhelmed. This should help gradually accustom the brain to handling a greater workload.
Every brain injury survivor will have a unique starting point. As long as you continue to challenge yourself by consistently practicing activities that require focus, your attention should improve.
Attention Problems After Brain Injury: Key Points
After a brain injury, individuals may experience a wide range of attention problems at varying severities. This is because many regions of the brain affect one’s ability to focus. Fortunately, there are several ways to help improve your focus so that you can overcome attention difficulties.
We hope this article has helped you understand why attention problems may occur after brain injury and how to successfully manage them.