Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for brain injury appears to offer many promising benefits. But what is oxygen therapy, and how does it work? That’s what we will discuss in this article.
To help you decide whether oxygen therapy is right for you, we’ll look at the science behind it, as well as the evidence both for and against its use in brain injury treatment.
Understanding Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Brain Injury
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen within an enclosed chamber for a specified amount of time, often for 1-2 hours, multiple days per week..The air in the chamber is pressurized at about two to three times the atmospheric pressure of sea level. The increased pressure compresses oxygen molecules, which lets the body absorb 10 to 15 times more oxygen than it does under normal pressure.
HBOT has proven effective at treating many different health conditions. Its primary use is treating people with decompression sickness (also known as the “bends”) but it’s also approved by the FDA to treat several other conditions, including carbon monoxide poisoning, radiation necrosis, and persistent wounds that will not heal.
Because oxygen therapy has proven effective in healing different types of wounds, many doctors believe that it could alleviate traumatic brain injury symptoms.
How Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Brain Injury Work?
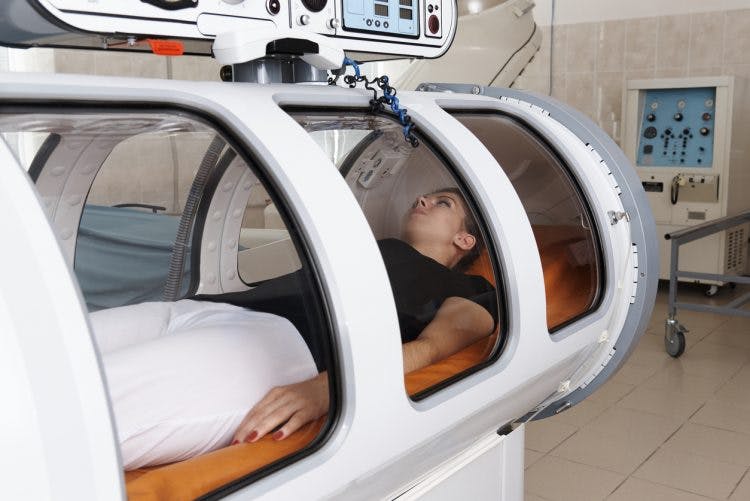

The human brain possesses its own natural repair mechanism, known as neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity is the process by which the brain rewires neurons to allow undamaged portions of the brain to take over function from damaged ones. And the main fuel for this process is oxygen.
Unfortunately, after an injury, the brain often cannot get enough oxygen to fuel its healing process. When a part of the body does not receive the right amount of oxygen, this leads to a condition known as hypoxia. Hypoxia slows down the healing process and, if left untreated, can trigger premature neuronal cell death (necrosis).
Hypoxia is one of the major secondary brain injuries that doctors try to prevent when treating someone with brain injury. However, once hypoxia sets in, it’s almost impossible to reverse.
That’s where hyperbaric oxygen therapy comes in. The idea is, if the brain receives enough concentrated oxygen, this will dramatically boost the healing process and prevent the effects of hypoxia.
Evidence for Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Brain Injury Patients
Recent studies have found that hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be able to promote brain recovery and neuroplasticity. The evidence for hyperbaric oxygen therapy for brain injury shows many positive benefits, including:
- Improves functional abilities. A 2022 study found that brain injury survivors who underwent hyperbaric oxygen therapy experienced lower levels of disability and improved self-care skills, even 6 months after completing their treatment. Furthermore, individuals who participated in hyperbaric oxygen therapy had higher levels of certain growth factors, such as BDNF and VEGF, which are essential for nerve and blood vessel growth and function.
- Boosts movement and cognition. A 2021 study including over 150 individuals with moderate to severe brain injuries revealed that hyperbaric oxygen therapy can improve movement and cognition, particularly when combined with twice daily intensive therapy.
- Improves post-concussive symptoms and emotional effects.. Another study examining the effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on mild TBI survivors demonstrated improvements in behavioral/emotional effects of brain injury, as well as a reduction in post-concussive symptoms. This included lowered depression and anxiety levels, improved sleep, and better quality of life. This study also found hyperbaric oxygen treatment improved memory and overall cognitive functioning.
- Better outcomes for both acute and chronic brain injury. While some studies have shown the beneficial effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy when used several months after their initial injury, others have also linked the treatment to improvements in the first several hours after brain injury. When used in the acute stages of brain injury recovery, HBOT may prevent secondary brain injuries from developing.
This evidence is certainly promising, but there are some caveats.
Evidence Against Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for TBI
On the other hand, some double-blind studies show no significant difference in improvement between those treated with HBOT and those who received a placebo treatment. This may indicate that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is not an effective treatment for brain injury patients.
Still, there is solid evidence from brain scans that demonstrate that hyperbaric oxygen therapy can indeed increase blood flow to the brain, which could have a positive impact on recovery. It’s important to note that even supporters of HBOT don’t believe it is useful on its own. Instead, they all agree it’s best used alongside traditional rehabilitation techniques.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Concussion
After a mild brain injury or concussion, some individuals may continue to experience symptoms for months or even years. These symptoms, often referred to as persistent post-concussion syndrome, may affect the individual’s quality of life, participation in daily tasks, and ability to return to work.
A 2022 systematic review examining 11 studies looking at the effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on persistent post-concussion syndrome found promising results for this population. Many individuals experienced improved symptoms, as well as cognitive benefits. Individuals who had post-traumatic stress syndrome along with persistent post-concussion syndrome tended to experience the most benefits. While the dosage varies by study, according to this systematic review it appeared that the optimal dosage of HBOT for improvements among individuals with concussions was 40 sessions at a pressure of 1.5 ATA.
By increasing the level of oxygen in the blood, several studies have found HBOT to be an effective treatment for relieving symptoms after concussion.
Is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Safe?

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is generally safe, though there are some minor risks involved, such as:
- Inner ear damage. Increased air pressure can cause middle ear damage and hearing problems. Fortunately, plugging your nose and blowing out air through it will typically relieve pressure in your ears and prevent damage.
- Seizures. Too much oxygen can trigger seizures in people with epilepsy after TBI. However, anti-seizure meds may be able to help with that.
Finally, people with claustrophobia or other anxiety disorders may have issues lying in an enclosed chamber. Fortunately, some facilities offer multiplace chambers, where multiple people can be undergoing treatment at the same time using specialized hoods or masks. This can also allow individuals to sit or even stand during their treatment.
Since no scientific consensus exists on the usefulness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for brain injury, the FDA has not officially approved it for TBI treatment. As a result, insurance and Medicare do not currently cover it. This means if you do try it, you will have to fund it yourself. However, there may be clinical trials available near you, which can enable you to access this therapy for free.
You’ll also want to make sure you receive oxygen therapy at a medical facility with a trained doctor on staff to consult with regarding the risks and benefits for your specific condition.
Is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Good for Brain Injury? A Therapist’s Perspective
As with all brain injury treatments, there is no “one size fits all” miracle cure. However, the research on hyperbaric oxygen therapy is promising. While it is not yet a fully approved treatment, there is a growing body of evidence on how HBOT can improve the secondary effects of brain injury, particularly cognition.
In acute brain injuries, HBOT can reduce mortality, however there may or may not be long-term benefits. Veterans with brain injuries may also benefit from HBOT, and are actually approved to receive HBOT treatments in several states.
While it is always best to talk with your doctor before starting any new treatments, the potential benefits combined with the limited side effects of HBOT make this treatment very appealing. If individuals feel that their recovery is slowing, adding HBOT alongside conventional rehabilitation may boost results. While some studies have suggested that improvements due to HBOT are due to a placebo effect, with the limited drawbacks, it may be worth trying if available in your area.
Consider checking out this link from the International Hyperbarics Association to read more about HBOT and its potential benefits for individuals with brain injuries. However, it should be noted that some of these articles may be slightly biased.
Should You Try Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Brain Injury?
In the end, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a relatively harmless therapy that could hold a lot of promise for brain injury patients, though the scientific verdict is still out.
The choice is ultimately up to you, but we hope this article has given you the information you need to make the best decision for your recovery.