Oxygen plays a central role in fueling cellular processes and fighting infections. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy allows the body to absorb more oxygen, which may help minimize damage following a spinal cord injury.
To determine if hyperbaric oxygen therapy is an effective treatment for spinal cord injuries, this article will discuss its procedure, risks, and benefits.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury
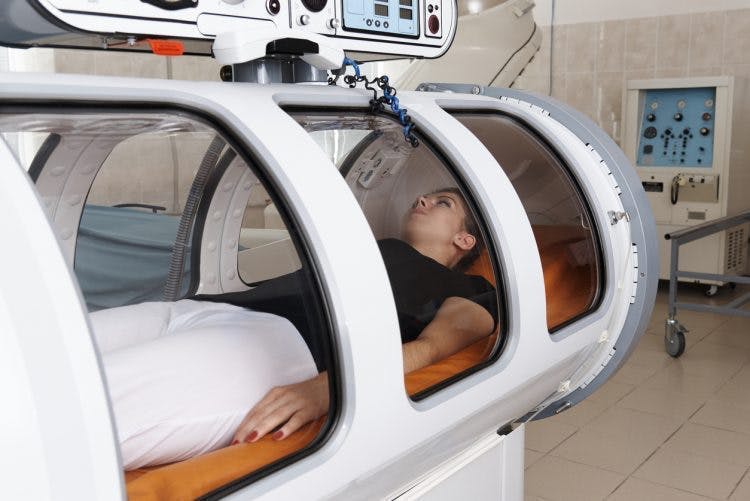
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a non-invasive procedure that involves exposure to 100% oxygen at two to three times normal air pressure. It can take place in a single unit or a room with several people.
Depending on the severity of the spinal cord injury, the number of recommended sessions and duration of treatment will vary. Generally, patients undergo 20-40 sessions lasting 60-120 minutes each. While hyperbaric oxygen therapy should not be painful, you may experience ear popping due to changes in air pressure.
After a spinal cord injury, a cascade of secondary processes occurs. If not promptly addressed, secondary processes can cause further damage to the spinal cord. It’s suggested that hyperbaric oxygen therapy can help minimize secondary damage by increasing the availability of oxygen in the body.
Rather than healing existing spinal cord damage, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is mainly intended to reduce the progression of damage.
Now that you understand what hyperbaric oxygen therapy is and its application, let’s discuss its benefits.
Benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury
While randomized controlled trials have yet to prove that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is an effective treatment for spinal cord injuries, experimental studies suggest that it can help regulate biochemical processes in the spinal cord.
Below, we’ll discuss 5 ways HBOT may be able to help minimize damage after a spinal cord injury.
1. Reduces Inflammation
Inflammatory processes following a spinal cord injury can cause swelling of the spinal cord. When excess swelling occurs, blood flow can be significantly reduced and individuals may experience spinal shock.
Spinal shock describes the temporary loss of all motor control and reflexes below one’s level of injury. Once the swelling is alleviated, reflexes may gradually return. However, this can take up to several months and delay the rehabilitation process.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy helps reduce inflammation by decreasing the spread of inflammatory mediators from damaged cells to surrounding healthy cells.
2. Decreases Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there’s an imbalance in the production of free radicals (highly reactive oxygen molecules) and antioxidant enzymes.
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals. When free radicals outnumber antioxidant enzymes, they can cause further damage to the spinal cord.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy helps activate the upregulation of antioxidant enzymes. The more antioxidants produced, the less reactive free radicals become, which helps reduce overall damage.
3. Minimizes Apoptosis
Inflammation and oxidative stress following a spinal cord injury can trigger the release of various enzymes and proteins that can activate apoptosis.
Apoptosis describes programmed cell deaths and while it occurs normally to regulate the number of cells in the body, too much apoptosis in the spinal cord can lead to significant neurological deficits.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy helps reduce apoptosis in the spinal cord by neutralizing oxidative stress and the expression of various enzymes that can activate apoptotic pathways.
4. Promotes Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the development of new blood vessels, which can help stabilize blood flow in the spinal cord.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy significantly increases levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is essential for promoting angiogenesis and neuroprotection. It helps restore blood supply in the spinal cord by increasing vascular density, which promotes neuronal protection and functional recovery.
5. Promotes Healing of Pressure Ulcers
Lack of motor control following a spinal cord injury increases one’s risk of developing pressure ulcers. Pressure ulcers occur when individuals sit or lie in the same position for too long. Prolonged pressure can cause tissue inflammation and skin breakdown in bony areas of the body.
Oxygen is essential for healing wounds like pressure ulcers. Therefore, exposure to 100% oxygen may be able to speed up the healing process.
For the treatment of pressure ulcers, topical application of oxygen is preferred. Rather than sitting in a chamber or breathing in oxygen from a face mask, the oxygen is directly delivered to the open wound.
Up next, we’ll discuss the side effects associated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Side Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury

While hyperbaric oxygen therapy appears to be a promising treatment for individuals with spinal cord injuries, it is not for everyone.
Side effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for spinal cord injury include:
- temporary nearsightedness from direct oxygen toxicity to the lens of the eye
- injury to the middle ear due to increased air pressure
- claustrophobia from being enclosed in the oxygen chamber
- lung collapse from changes in air pressure
- seizures from overdosing on oxygen (oxygen toxicity)
As a result, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may not be ideal for patients following spinal cord injury who have respiratory complications or anxiety. To make sure it is safe for your specific spinal cord injury, consult with your doctor.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for SCI: Key Points
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy helps the body absorb greater amounts of oxygen, which may help minimize damage after a spinal cord injury.
Due to limited research, HBOT is not an FDA-approved treatment for spinal cord injury and is used off-label. While many experimental studies show promising results, clinical reports show mixed evidence.
We hope this article helped you understand what hyperbaric oxygen therapy is and how it can help individuals with spinal cord injuries recover.