The primary goals of spinal cord injury treatment are to help minimize complications and promote functional independence.
Every spinal cord injury is unique, so a personalized approach to rehabilitation that targets each individual’s specific weaknesses is essential. Many factors such as the level and severity of injury, secondary complications, mental health, and intensity of rehabilitation therapies can affect recovery outcomes.
This article will discuss various treatment interventions that can help spinal cord injury patients maximize their functional independence, including:
- Treatments to stabilize the spinal cord
- Rehabilitative spinal cord injury treatments
- Complementary and alternative medicine practices
- Spinal cord injury treatments in progress
Treatments to Stabilize the Spinal Cord
The first step in treating a spinal cord injury is to minimize the onset of secondary damage by stabilizing the spinal cord.
Damage to the spinal cord consists of 2 phases: primary and secondary injury. Primary damage is the direct result of the traumatic event that compresses the spinal cord. In contrast, secondary damage describes the damage your spinal cord experiences in the hours to weeks following the initial injury. Examples of secondary damage include reduced blood flow, swelling, cell deaths, and excitotoxicity.
While primary damage cannot be prevented, immediate medical attention following a spinal cord injury can significantly minimize the progression of secondary damage.
Treatments to stabilize the spinal cord may include:
- Surgery is sometimes performed to decompress the spinal cord and realign the spine. This will help alleviate pressure from the spinal cord and improve blood circulation.
- Corticosteroids like Methylprednisolone have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce swelling in the spinal cord.
- Immobilization of the spinal cord may be necessary, with traction, a neck collar, and/or a special bed.
- Ventilators may be necessary to breathe after a higher-level (C1-C5) spinal cord injury that affects control of the diaphragm.
Now that you understand what treatments help stabilize the spinal cord immediately after injury, let’s discuss rehabilitation treatments.
Rehabilitative Spinal Cord Injury Treatments

One major barrier to spinal cord injury treatment is that damaged neurons in the central nervous system cannot regenerate. Fortunately, the central nervous system has neuroplasticity (the ability to adapt and reorganize itself), which allows individuals to recover functions affected by spinal cord injury.
However, only healthy, undamaged neural pathways in the spinal cord are capable of neuroplasticity. The less severe a spinal cord injury is, the more spared neural pathways exist, and the better the potential for recovery.
Because the spinal cord adapts based on demand, highly-repetitive and task-specific movements are essential for promoting neuroplasticity. Consistent stimulation will help the spinal cord perceive a demand for that function and prompt circuit reorganization.
Below, we’ll discuss several rehabilitative treatments that can help spinal cord injury patients promote neuroplasticity.
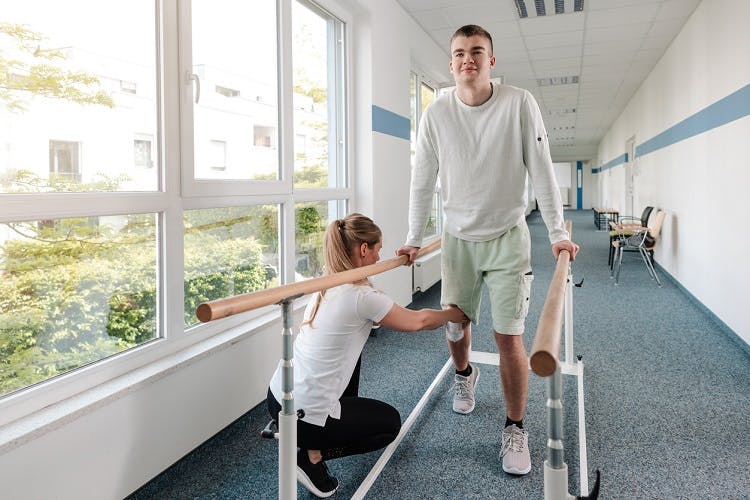
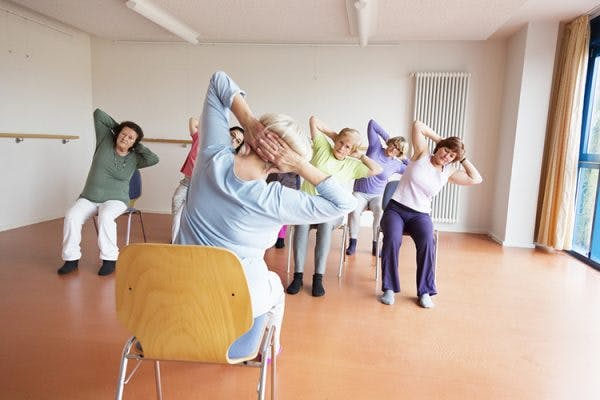
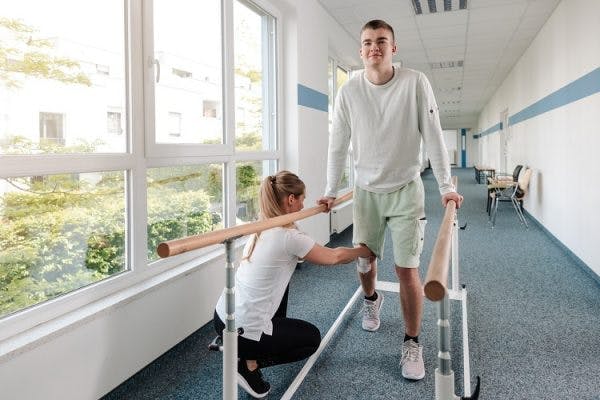
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is the foundation of spinal cord injury rehabilitation. It focuses on improving mobility through targeted exercises.
A physical therapist will evaluate your functional abilities and create a personalized exercise regimen designed to maximize range of motion, strengthen the muscles, and improve movement patterns.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy teaches individuals how to regain their independence by practicing activities of daily living such as transferring (moving from one surface to another), toileting, and grooming. It can also involve learning how to use adaptive tools to compensate for limited mobility.
Speech Therapy
If your injury resulted in any respiratory complications, then you may need to work with a speech therapist to improve your breath support, increase cough strength, and teach you how to manage secretions.
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
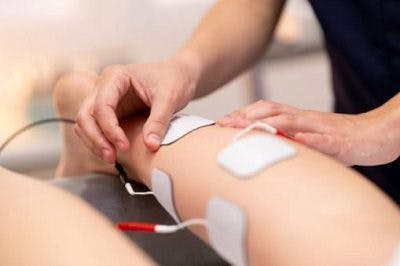
Functional electrical stimulation is a non-invasive treatment that involves placing electrodes on the surface of the skin while the patient performs a task.
The electric currents mimic brain signals and cause the muscles to contract. By directly activating muscle contractions, FES can help improve circulation, range of motion, and muscle strength.
Muscle Relaxants/ Botox
Spasticity (involuntary muscle contractions) is a major complication of spinal cord injury that can cause stiffness and limited mobility. Muscle relaxants or Botox injections can help temporarily reduce the effects of spasticity by blocking the signals that trigger muscle contractions.
Spinal cord injury patients should take advantage of their reduced spasticity while using muscle relaxants or Botox to focus on performing the exercises necessary to promote neuroplasticity and improve long-term mobility.
The following section will discuss alternative treatments for spinal cord injury.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine for Spinal Cord Injury
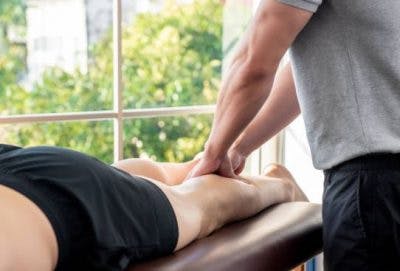
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) refers to therapies that are not associated with conventional medical treatment. Adding CAM practices to your spinal cord injury treatment plan may help relieve complications like pain, fatigue, and anxiety.
Examples of CAM therapies include:
- Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese practice that involves placing hair-like needles into specific acupoints for therapeutic relief. In Western countries, acupuncture has been adopted as a technique for pain relief, but in the East, it’s used to treat a variety of neurological problems.
- Massage therapy helps stimulate blood flow, which increases the body’s ability to absorb oxygen into the tissues. It also relaxes the muscles and relieves tension, which can help reduce pain and improve range of motion.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves breathing in pure oxygen at increased pressures. Oxygen plays an essential role in cellular activity and may help reduce secondary damage after a spinal cord injury by reducing swelling, promoting tissue growth, and increasing the production of antioxidant enzymes.
- CBD products allow SCI patients to benefit from the pain-relieving properties of marijuana while avoiding its psychoactive effects.
Minimizing complications of spinal cord injury can help promote better focus and performance in rehabilitation therapies.
Up next, we’ll discuss 2 promising treatments that may help further recover motor control and sensation after SCI.
Spinal Cord Injury Treatments in Progress

Current research for spinal cord injury treatment predominantly focuses on epidural stimulation and stem cell transplantation.
Epidural stimulation involves implanting an electrode array onto the lower spine. It stimulates movement by working around the spinal cord damage and exciting electrons below the level of injury.
In contrast, stem cell therapy is intended to promote the regeneration of damaged spinal cord tissues. Because stem cells can divide infinitely and differentiate into various cell types depending on their surrounding environment, they show great potential as a treatment for spinal cord injuries.
While both of these treatments are promising, they require larger-scale research and development to determine factors like ideal dosage, length of treatment, and safety protocols.
Spinal Cord Injury Treatments: Key Points
While damage caused by a spinal cord injury can’t be reversed, there are treatments that can help reduce complications and improve mobility.
Additionally, innovative research shows promising results that suggest a hopeful future for spinal cord injury recovery.
Hopefully, this article provided helpful insight into the spinal cord injury rehabilitation process. Good luck!