Stem cell therapy is an exciting breakthrough in brain injury treatment. While most stem cell therapies for brain injury patients are still in the clinical trial phase, the results so far have been very promising.
Today’s article will explain what stem cell therapy is and how it can help treat traumatic brain injury.
We’ll also look at what the most recent studies say and how you can take part in this cutting-edge therapy.
What are Stem Cells?
Before you can understand how stem cell therapy for brain injury works, let’s discuss the basics of stem cells.
Stem cells are a class of undifferentiated cells that can transform into specialized cell types. They are the raw material that the body uses to create every other cell. This means that stem cells can become any type of cell under the right conditions, including brain cells.
There are three main sources of stem cells that researchers have discovered:
- Embryonic stem cells. These stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old.
- Adult stem cells. These are found in adult tissue such as bone marrow or fat.
- Perinatal stem cells. Finally, researchers have found stem cells in amniotic fluid and even umbilical cord blood.
For brain injury treatment, most clinical trials have used adult stem cells.
How Stem Cell Therapy for Brain Injury Patients Works
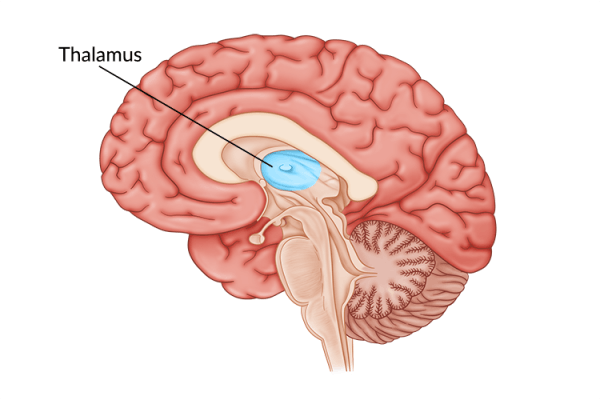
After traumatic brain injury, damage to brain tissue can cause brain cells to die.
When neurons die, they cannot regenerate or be replaced. Dead neurons also lead to loss of function, since brain signals can no longer pass through them.
Because neurons cannot regenerate on their own, most forms of brain injury treatment focus on activating neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity involves reorganizing surviving brain cells.
To understand how this works, imagine that the brain is a series of highways and bridges. The bridges (neurons) allow cars (nerve signals) to quickly travel where they need to go. If these bridges collapse, however, then the signals can no longer travel.
Neuroplasticity, which allows the brain to establish new neural pathways, is like building a detour to help cars get around the broken road. Stem cell therapy, on the other hand, is the equivalent of rebuilding the broken bridge.
That’s because stem cells can, with the right conditions, help the brain replace the neurons that were destroyed.
Therefore, this therapy can potentially help brain injury patients regenerate the damaged parts of their brain and recover function.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works
During stem cell therapy, neurosurgeons transplant stem cells (harvested from the patient’s own bone marrow) into the damaged areas of the brain.
Interestingly, in a recent study by the SanBio Group, the stem cells used did not turn into neurons themselves. Rather, the implanted cells triggered the brain’s natural regenerative ability and, in effect, helped the brain create its own new neurons.
As Dr. Gary Steinberg, lead researcher on another stem cell project, explains:
What these [stem cells] do is pump out very powerful growth factors, molecules, and proteins that enhance recovery…and in that way, what we believe they do is turn the adult brain into a neonatal or infant brain, which has a lot of ability to recover after brain injury.
In other words, stem cell therapy doesn’t just replace damaged neurons. It essentially reverses the aging process in the brain and makes it a powerhouse of cell regeneration.
What Do Studies Show?

In the study linked to above, 46 TBI patients were treated with an investigational stem cell product, and 15 underwent sham surgery as a control group.
Improvement was measured by a change in the Fugl-Meyer Motor Scale score, a test used to measure movement deficits. An improvement of ten or more points is considered a clinically meaningful threshold in TBI patients.
Overall, 18 patients treated with stem cell therapy reached this threshold, compared to one placebo patient.
To put these numbers in a more practical perspective, one patient who could not move their arm at all recovered full arm function. Others improved their balance skills and could even walk again after using a wheelchair.
These results are impressive, but the study was small and is still in phase 2 of clinical trials. More data is still needed to make sure the therapy is safe for the general population. But so far, the evidence is promising.
How to Access Stem Cell Therapy for Brain Injury
Currently, stem cell therapy has not received FDA approval for use in brain injury treatment. This means the best way to gain access to stem cell therapy is to enroll in a clinical trial.
Clinical trials are not always free. However, most trials are federally funded so there is often little to no cost.
In contrast, stem cell therapies for other conditions typically range between $3,000-$5,000 dollars. Since stem cell therapy for TBI will also involve brain surgery, it could potentially cost even more. In order to save money, try to find a clinical trial that you qualify for.
To find a clinical trial near you, go to the clinical trials website and type in “traumatic brain injury” under the conditions or disease bar. Then, type in “stem cell” under the other terms bar and click search.
As of this writing, there are currently six clinical stem cell therapy trials in the United States actively recruiting TBI patients. Hopefully one of those will be near you.
Hope for Recovery Without Stem Cell Therapy

If you cannot afford stem cell therapy for brain injury and there are no clinical trials open, do not despair. There is still hope for recovery.
Because of the brain’s neuroplasticity, you can continue to regain function, even if it has been years since your injury.
Many doctors used to tell their patients that TBI recovery stalls after two years. However, recent research has challenged this wisdom and shows that recovery does, in fact, continue past those first 2 years.
For example, a study that followed TBI patients for a decade found that, even at the 10-year mark, some patients were still improving their function.
In fact, several, when they were examined after 2 years and 5 years, still needed assistance with daily activities. But by 10 years, those same patients had finally regained functional independence.
Therefore, it is crucial to learn how to continue to recover from brain injury and to follow that formula. The more consistently you keep up with your therapy, the more progress you will make. No matter how long it has been.
Stem Cell Therapy for Brain Injury: Key Points
Stem cell therapy is a promising new treatment that may revolutionize brain injury rehabilitation.
It works by transplanting stem cells from the person’s bone marrow into damaged parts of their brain. These stem cells trigger neuron regeneration and help patients recover function.
This makes stem cell therapy potentially one of the most groundbreaking treatments for TBI.
However, even if you can’t access stem cell therapy, the brain can still recover function through other means. Therefore, until stem cell therapy is more widely available, TBI survivors should continue with their traditional therapy programs.
With enough persistence, you can make real, permanent gains in your recovery process. That’s the power of consistent therapy.