Have you ever felt like you’re looking right at something but just not seeing it? Maybe you’ve bumped into furniture on one side of a room or missed a friend waving hello on your left. For some individuals, this isn’t just a momentary lapse. It could be a sign of something called visual neglect or inattention. But what’s the difference between visual neglect vs inattention?
These two terms are often used in discussions about attention and perception, particularly after neurological events like a stroke or brain injury. However, while they can sometimes overlap, they represent distinct challenges in how the brain processes visual information.
In this article, we’ll explore visual neglect and inattention—what they are, how they differ, and practical steps individuals can take to manage these conditions.
What is Visual Inattention? The Scattered Spotlight
Imagine your attention as a spotlight. Normally, you can direct this spotlight wherever you need it – focusing on a specific object, a conversation, or a task at hand. Visual inattention, also sometimes referred to as visual attentional deficits, is like having a scattered or unstable spotlight.
With visual inattention, the individual has difficulty focusing and sustaining their attention on visual stimuli. They might:
- Miss details: They might scan a scene but fail to notice important elements, like a word in a sentence or a face in a crowd.
- Be easily distracted: External stimuli, like a noise or movement in their peripheral vision, can easily pull their attention away from what they were initially focused on.
- Have trouble filtering information: They might struggle to ignore irrelevant visual information and focus on what’s important.
- Show inconsistent performance: Their ability to notice things might fluctuate depending on their level of alertness, motivation, or the complexity of the visual environment.
Think of it like trying to read a book in a busy coffee shop. The surrounding conversations, the clinking of cups, and the movement of people can all pull your attention away from the text, making it harder to concentrate and understand. For someone with visual inattention, this struggle can be amplified and more persistent, even in less distracting environments.
What is Visual Neglect? The Ignored Half of the World
Visual neglect, on the other hand, is a more profound and often more debilitating condition. Unlike inattention, which is a problem with focusing, neglect involves a lack of awareness of stimuli on one side of the visual field – even though the eyes themselves are perfectly capable of seeing.
Imagine your visual world divided into two halves – left and right. For someone with visual neglect, it’s as if one of these halves simply doesn’t exist.
For example, they might:
- Fail to notice objects on the affected side: This can range from not seeing food on one side of their plate to bumping into doorways or people on their neglected side.
- Not respond to stimuli on the affected side: If someone speaks to them from their neglected side, they might not turn their head or acknowledge them.
- Only draw or copy one side of an image: When asked to draw a clock, for example, they might only draw the numbers on the right side.
- Read only one side of a page: They might start reading in the middle of a sentence or only read the words on the non-neglected side.
- Neglect one side of their own body: In severe cases, they might even forget to groom or dress the neglected side of their body.
The key difference here is that with visual neglect, the information from the affected visual field isn’t even being processed by the brain in a way that leads to awareness. There is evidence that many cases of visual neglect also involve multisensory aspects, particularly auditory deficits. It’s not just a matter of difficulty focusing. It’s as if that part of the visual world has been erased from their conscious experience.
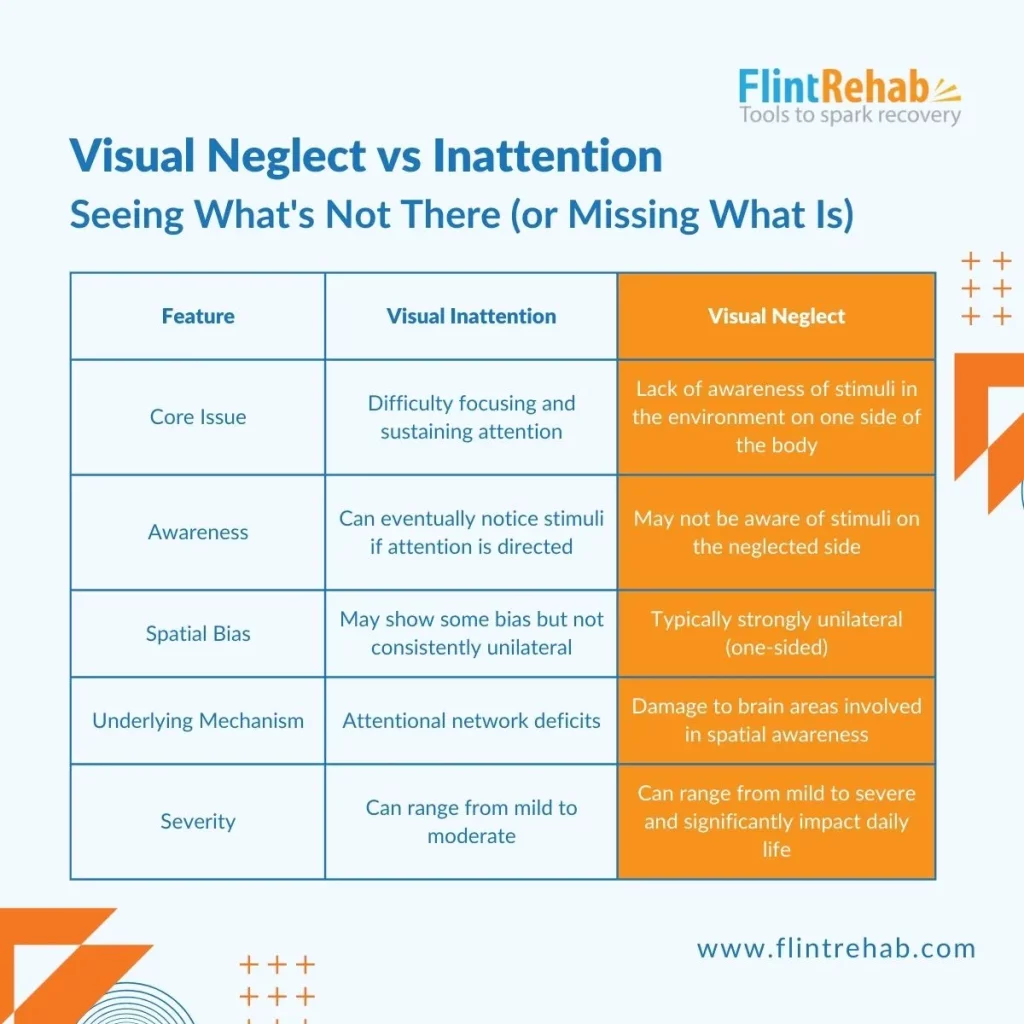
Visual Neglect vs Inattention Key Differences
To make the distinction clearer, let’s use a simple analogy:
Visual Inattention: Imagine a spotlight that keeps flickering and jumping around, making it hard to keep it focused on one thing. The information is there, but the spotlight isn’t steady enough to illuminate it consistently.
Visual Neglect: Imagine a blind spot in your vision. No matter how hard you try to focus, you simply cannot see what’s in that area. The information isn’t even reaching your conscious awareness.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
What Causes Visual Neglect vs Inattention?
Both visual inattention and neglect are often the result of a neurological injury, most commonly stroke. Other injuries such as TBI, tumors, and other neurological conditions can also cause visual neglect and inattention.
Generally, the specific areas of the brain affected for visual neglect vs inattention tend to differ. This leads to the different symptoms and presentation for each.
Visual inattention is often associated with damage to the frontal and parietal lobes, which play crucial roles in attention control, executive functions, and the filtering of information. Damage to these areas can disrupt the brain’s ability to direct and maintain focus on visual stimuli.
Conversely, visual neglect is most commonly linked to damage in the posterior parietal lobe, particularly in the right hemisphere. This area is critical for spatial awareness and the representation of space. Damage here can disrupt the brain’s ability to process information from the contralateral (opposite) side of the body and visual field. Right hemisphere damage often leads to left-sided neglect, which is more common and often more severe than right-sided neglect.
It’s important to note that there can be overlap, and an individual might experience both inattentive tendencies and some degree of neglect, especially in the acute stages after a brain injury.
Living with Visual Inattention and Neglect: Challenges and Adaptations
Living with visual inattention or neglect can significantly impact daily life. For example, imagine trying to navigate a crowded street when you constantly miss people walking on one side or trying to read an email when your attention keeps drifting away.
Here is an overview of some challenges individuals with visual inattention or neglect may face.
Visual Inattention Challenges May Include:
- Difficulty with tasks requiring sustained visual focus, such as reading, writing, or computer work.
- Increased risk of errors and accidents due to missed details.
- Challenges in social situations due to difficulty following conversations and noticing non-verbal cues.
- Frustration and fatigue due to the constant effort required to maintain focus.
Visual Neglect Challenges May Include:
- Difficulties with basic self-care activities like eating, dressing, and grooming the neglected side of the body.
- Increased risk of falls and collisions due to a lack of awareness of obstacles on the neglected side.
- Challenges with navigation and mobility in both familiar and unfamiliar environments.
- Difficulties with reading and writing, often leading to significant communication challenges.
- Social isolation due to difficulties interacting with others and navigating social situations.
Despite these challenges, individuals with visual inattention and neglect can learn to adapt and improve through various rehabilitation strategies.
Visual Neglect vs Visual Inattention Rehabilitation and Management: Retraining the Brain
The good news is that the brain has a remarkable capacity for recovery and adaptation, a concept known as neuroplasticity. While complete recovery may not always be possible, various therapeutic interventions can help individuals with visual inattention and neglect improve their awareness and function.
Let’s take a look at some strategies you can use to manage or improve both visual inattention and neglect.
Rehab and Management Strategies for Visual Inattention
Attention Training Exercises: These exercises aim to improve sustained, selective, and divided attention through tasks that gradually increase in complexity.
Environmental Modifications: Reducing distractions and organizing the environment can help minimize attentional demands.
Compensatory Strategies: Using techniques like verbal self-instruction, scanning strategies, or visual cues to help maintain focus.
Medication: In some cases, medication may be used to address underlying attentional deficits.
Rehab and Management Strategies for Visual Neglect
Visual Scanning Training: Encouraging systematic scanning of the neglected side by providing visual cues and feedback.
Prism Adaptation: Using prism glasses that shift the visual field to the non-neglected side, which can temporarily improve awareness of the neglected side and have lasting effects.
Limb Activation Therapy: Encouraging movement of the limb on the neglected side to increase awareness of that side of the body and space.
Environmental Adjustments: Placing important items on the non-neglected side initially and gradually encouraging scanning to the neglected side.
Virtual Reality Therapy: Offering immersive and engaging environments to practice scanning and navigation skills.
Researchers are continuing to examine which methods are most effective for treating visual inattention and neglect. For anyone experiencing visual inattention or neglect, it’s helpful to work with your care team of specialists. These professionals can help create a personalized rehab plan just for you!
Living With Visual Neglect and Inattention: Final Thoughts
Visual inattention and visual neglect are distinct but related conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perceive and interact with the world around them. While both involve challenges with visual processing, inattention is primarily a difficulty with focusing attention, while neglect involves a lack of awareness of one side of the visual field.
Understanding these differences is critical to effective rehabilitation and providing appropriate support to individuals living with these conditions. If you or someone you know is experiencing difficulties with attention or seems unaware of one side of their environment, it’s essential to seek professional medical advice. Early diagnosis and intervention can make a significant difference in improving quality of life and fostering greater independence.
The brain is amazing and can bounce back in incredible ways. With the right support and strategies, individuals with neglect or inattention can find new ways to navigate the world and keep moving forward.